Master Cybersecurity with Cloud Computing: Essential Course

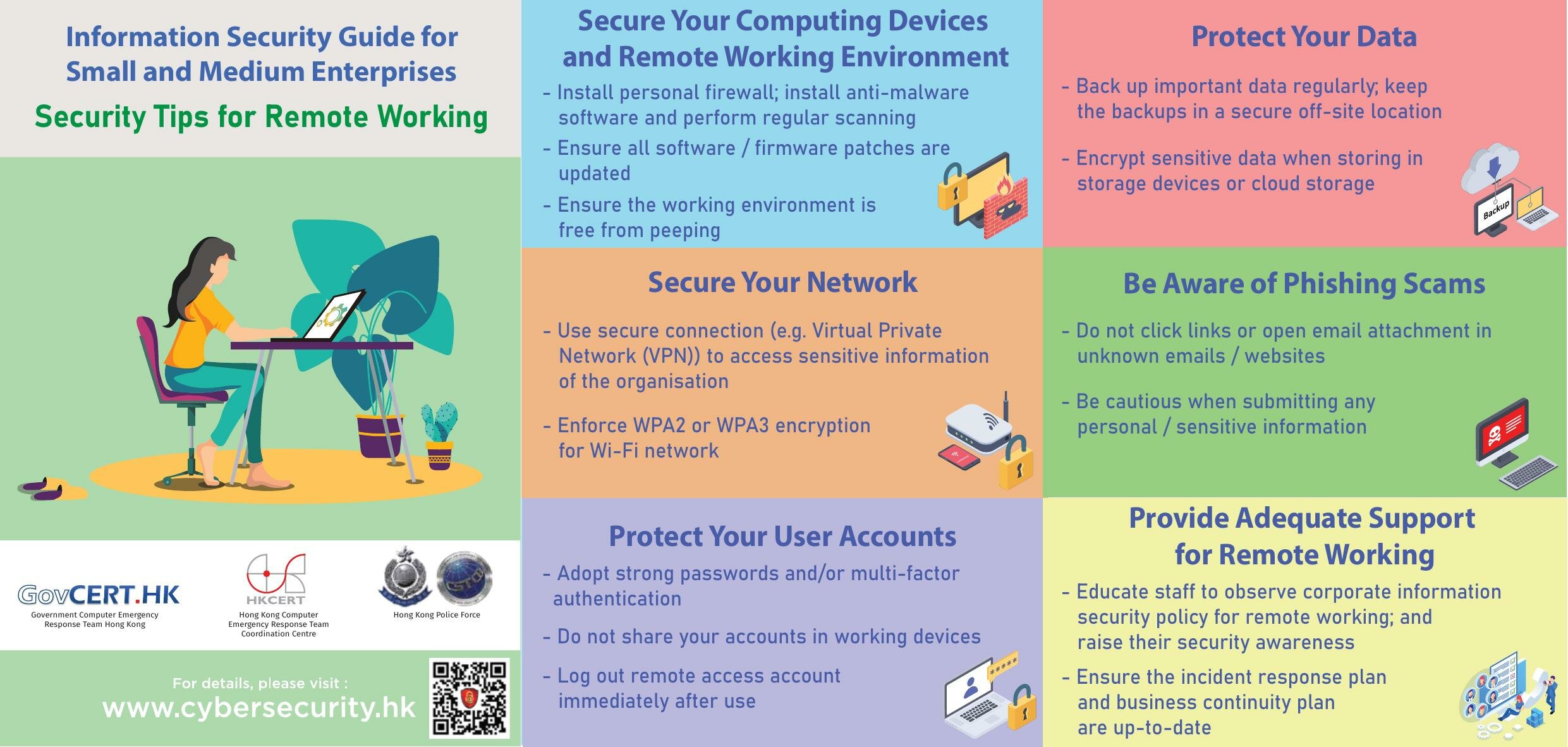
Mastering cybersecurity in the age of cloud computing has become critical for any organization's digital safety framework. As we embrace the digital transformation, understanding how to secure cloud environments from threats is paramount. This guide will take you through key strategies and technologies that bolster cybersecurity within cloud infrastructures, ensuring your business is protected while reaping the benefits of cloud computing.
Understanding Cloud Security
Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, but it also introduces unique security challenges. Here are the foundational aspects of cloud security:
- Data Breaches: With cloud services hosting vast amounts of data, breaches are a major concern.
- Compliance and Governance: Ensuring that cloud operations comply with various industry standards and regulations.
- Insider Threats: Unauthorized access by employees or insiders poses risks to cloud data.
- Multi-tenancy: Cloud environments share resources among multiple users, which can compromise security if not managed correctly.

🔍 Note: Security in cloud environments should be an integral part of any cloud strategy, not an afterthought.
Key Security Practices for Cloud Computing
To effectively secure cloud environments, consider implementing these practices:
- Encryption: Use encryption for data at rest and in transit to protect from unauthorized access.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implement stringent policies to manage access, using principles like least privilege.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic security audits and penetration testing to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
- Network Security: Use tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure VPN connections.
- Monitoring and Logging: Deploy comprehensive logging and monitoring systems to track suspicious activities and anomalies.
Securing your cloud environment involves not just technological solutions but also robust policies, training, and awareness:
- Security Training: Train staff on best security practices in cloud computing.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a clear, actionable plan for security incidents.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Ensure data is backed up regularly and there’s a recovery plan in place.
Cloud Security Solutions
Several security solutions are tailored for cloud environments:

| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) | Intermediaries that enforce security policies between cloud consumers and providers. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Provides real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. |
| Encryption Services | Services like AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault manage encryption keys for cloud data protection. |
🔍 Note: Tools should be selected based on the specific needs of the cloud environment, considering factors like compliance, data sensitivity, and infrastructure size.
Compliance and Standards
Ensuring cloud security also means adhering to international standards and regulations:
- ISO 27001: A globally recognized standard for managing information security.
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation affects how data is handled, especially for EU citizens.
- HIPAA: U.S. healthcare industry standard for protecting patient information.
Future Trends in Cloud Security
Here are some evolving trends:
- Zero Trust Models: Moving away from the traditional perimeter security to a model where every access request is thoroughly vetted.
- AIOps: Leveraging AI for IT operations to enhance security through predictive analytics and automation.
- Decentralized Identity: Using blockchain to manage identity in cloud systems for a more secure access control system.
- Quantum Computing: Preparing for the potential of quantum computing to decrypt current encryption methods.
In wrapping up, mastering cybersecurity in cloud computing involves understanding the unique threats posed by cloud environments, implementing robust security practices, using specialized tools, and staying ahead of emerging trends. By taking a proactive approach, businesses can not only protect their cloud infrastructure but also ensure compliance and build customer trust. It's about creating a resilient cloud environment that can adapt to the dynamic nature of cyber threats.
What is the Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Security?
+Cloud security is managed through a shared responsibility model where cloud providers secure the infrastructure (like hardware, software, networking), while customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, access management, and other services they manage on the cloud.
How can encryption protect my cloud data?
+Encryption makes data unreadable without the correct keys, ensuring that even if there is a data breach, the data remains protected from unauthorized access or use. Cloud services often provide built-in encryption options for both data at rest and in transit.
What are the main cloud deployment models?
+The main cloud deployment models include:
- Public Cloud: Services are provided over the internet to the general public.
- Private Cloud: Infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization for more control and security.
- Hybrid Cloud: A mix of both public and private cloud to meet varying needs.
- Multi-Cloud: Using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance resilience.
What are the benefits of using a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)?
+CASBs help by:
- Enforcing security policies and compliance across cloud services.
- Providing visibility into cloud usage and potential threats.
- Protecting against data leakage through cloud applications.
- Managing access control, encryption, and data loss prevention.
How do AI and machine learning enhance cloud security?
+AI and machine learning improve cloud security by:
- Automating threat detection and response through pattern recognition and anomaly detection.
- Enhancing user behavior analytics to identify deviations from normal activity.
- Predictive analytics to anticipate security threats before they occur.
- Automating security policy enforcement and reducing false positives in security alerts.
Related Terms:
- microsoft azure cyber security training
- cloud security essentials training
- azure cloud security certification
- aws cloud security course
- microsoft azure cyber security tools