Cloud Computing: Fortifying Your Security in the Digital Age

Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and application deployment. However, with this convenience comes the critical challenge of ensuring robust cloud security. This blog post will delve into the importance of cloud security, explore common threats, outline best practices, and discuss the latest tools and strategies to protect your cloud environment in the digital age.
Why Cloud Security is Paramount
In an era where data breaches can cripple organizations, the security of cloud environments is no longer just an IT concern but a strategic business imperative. Here’s why cloud security is more crucial than ever:
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require strict adherence to laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, which mandate secure handling of data.
- Data Sensitivity: With sensitive information moving to the cloud, protecting against unauthorized access is vital.
- Shared Responsibility Model: Cloud providers secure the infrastructure, but application and data security remain largely with the customer.
- Cost of Breaches: Security incidents can lead to massive financial losses due to downtime, legal fees, and reputational damage.

Common Security Threats in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing environments face numerous threats. Here are some of the most prevalent ones:
- Data Breaches: Malicious actors attempt to access sensitive data stored in the cloud.
- Insider Threats: Employees or insiders with malicious intent can compromise cloud security.
- Insecure APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that aren’t properly secured can be entry points for attackers.
- Misconfiguration: Incorrect setup of cloud services can lead to vulnerabilities.
- Shared Technology Vulnerabilities: Flaws in cloud infrastructure shared by multiple tenants.
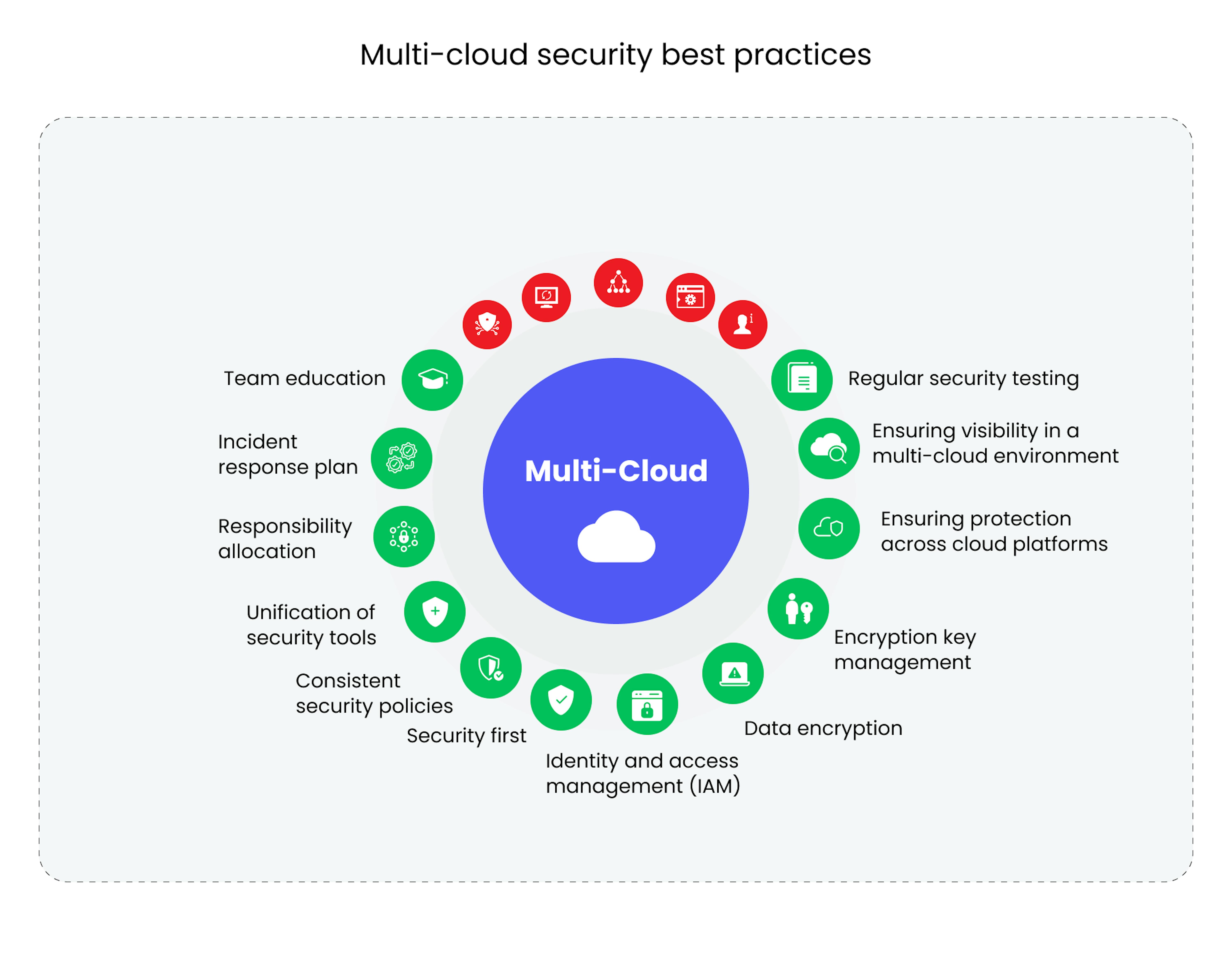
Best Practices for Cloud Security
To safeguard against these threats, organizations must implement the following best practices:
- Encryption: Use strong encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and least privilege principles.
- Regular Audits and Compliance: Conduct periodic security audits, penetration testing, and adhere to compliance standards.
- Endpoint Protection: Ensure all devices accessing the cloud are secure with up-to-date security measures.
- Monitoring and Logging: Enable continuous monitoring and logging of all cloud activities for real-time threat detection.
🔒 Note: Encrypting sensitive data in the cloud not only protects it against breaches but also fulfills regulatory requirements.
Tools and Technologies for Cloud Security
Utilizing the right tools and technologies can significantly enhance your cloud security posture:

| Tool/Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| AWS CloudTrail | Logs, monitors, and retains events related to actions across your AWS infrastructure. |
| Azure Security Center | Provides threat detection, advanced analytics, and threat intelligence for Azure resources. |
| Cloudflare | Offers DDoS protection, DNS filtering, and secure CDN services. |
| Splunk | A security information and event management (SIEM) tool for real-time monitoring and analytics. |
Navigating the Future of Cloud Security
As cloud environments evolve, so too must security strategies:
- Automation: Automate repetitive security tasks like compliance checks and patch management.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Adopt a “never trust, always verify” approach to prevent lateral movement in the network.
- AI and Machine Learning: Use AI to predict, detect, and respond to threats in real-time.
- Serverless Security: With serverless computing, traditional perimeter security measures need reevaluation.
In this digital age, cloud security isn't just about protecting assets; it's about ensuring business continuity, maintaining customer trust, and complying with laws. By recognizing the shared responsibility in cloud environments, employing stringent security practices, and leveraging modern tools, businesses can fortify their cloud infrastructure against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. This comprehensive approach will not only enhance security but also position the company for future growth and innovation in the cloud ecosystem.
What are the benefits of using cloud security solutions?
+Cloud security solutions offer scalability, managed security updates, enhanced monitoring capabilities, and access to advanced security features like AI-driven threat detection and analytics.
How does encryption help in cloud security?
+Encryption transforms data into unreadable cipher-text, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or accessed unauthorizedly, it remains protected from prying eyes.
What is the Zero Trust Security Model?
+The Zero Trust Security Model operates on the principle of inherent distrust, requiring continuous verification of identity and security posture regardless of location or network. It assumes breach and verifies each transaction as if it originates from an uncontrolled environment.