Top Strategies for Securing Your Cloud Computing Environment
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, with the rise in cloud adoption, ensuring the security of cloud environments has become more critical than ever. This post will delve into the top strategies for securing your cloud computing environment, providing actionable steps to enhance your cloud security posture.
Understanding Cloud Security
Before diving into specific strategies, let's first understand what cloud security entails. Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and the infrastructure associated with cloud computing. It includes policies, controls, and procedures designed to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud services.
Key elements of cloud security include:
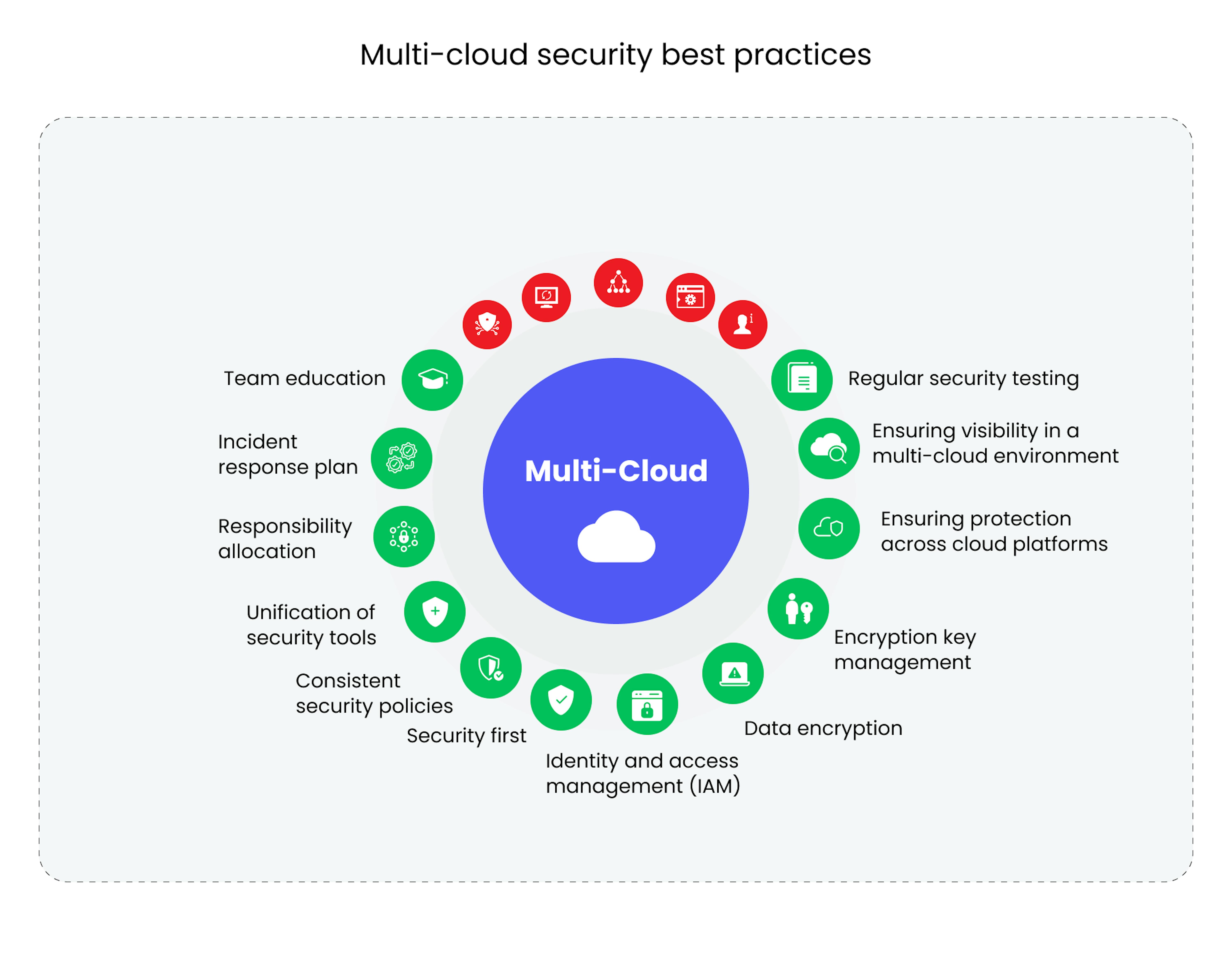
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Data Encryption
- Network Security
- Compliance and Governance
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Top Strategies for Cloud Security
1. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the cornerstone of cloud security:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require users to verify their identity through multiple verification methods.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Ensure users are granted only the permissions they need to perform their roles.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Review access permissions periodically to ensure compliance with organizational policies.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Implement SSO to streamline access while maintaining security.
🔒 Note: Always use secure channels for authentication; phishing-resistant MFA methods like U2F keys or app-based authenticators are highly recommended.
2. Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption is vital for protecting your data:
- Encrypt Data at Rest: Use encryption for data stored in cloud services like Amazon S3 or Azure Blob Storage.
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Use protocols like TLS/SSL to secure data moving between clients and cloud services.
- Key Management: Manage encryption keys securely using cloud provider services or third-party solutions.
3. Network Security
Securing your network in the cloud involves:
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Isolate resources by creating private networks within the cloud environment.
- Firewalls and Security Groups: Control inbound and outbound traffic with firewall rules.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Protection: Leverage cloud provider tools to mitigate DDoS attacks.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Implement these strategies to keep your cloud secure:
- Log Analysis: Regularly analyze logs to detect unusual activities or potential security incidents.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Use SIEM to aggregate and analyze security logs from multiple sources.
- Automated Threat Detection: Utilize AI and machine learning tools for predictive security analytics.
5. Patch Management and Vulnerability Assessment
Keeping systems up-to-date is crucial:
- Automated Patching: Use tools that automatically apply security patches to your cloud infrastructure.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct regular scans to identify and remediate vulnerabilities.
- Policy as Code: Implement infrastructure as code to enforce security policies uniformly across your cloud environment.
6. Security Compliance and Governance
Compliance ensures adherence to legal and regulatory standards:
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): Implement CASB to monitor activities and enforce security policies.
- Compliance Frameworks: Adhere to frameworks like ISO 27017, SOC 2, or HIPAA where applicable.
- Regular Compliance Audits: Perform internal and external audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
📝 Note: Compliance should be viewed as a dynamic process, adapting to new regulations and cloud provider updates.
In Conclusion
Securing your cloud computing environment is a multifaceted endeavor requiring a combination of strategic planning, technical solutions, and ongoing vigilance. By implementing robust IAM, ensuring data encryption, maintaining strong network security, continuously monitoring for threats, staying vigilant with patch management, and aligning with compliance requirements, businesses can safeguard their cloud assets effectively. Remember, security in the cloud is not a one-time setup but an ongoing commitment to protect your digital infrastructure against evolving threats.
What are the benefits of cloud security?
+Cloud security offers benefits like protection from data breaches, regulatory compliance, scalable security solutions, cost efficiency through reduced need for physical security infrastructure, and the ability to manage security across distributed environments.
How often should security audits be conducted?
+Security audits should be conducted at least annually, but more frequent audits might be necessary for environments handling sensitive data or in highly regulated industries. Real-time monitoring should also be part of your strategy.
Can cloud security be DIY or do you need specialized services?
+While basic security measures can be implemented DIY, for complex environments or higher security needs, specialized cloud security services or managed security providers can offer expertise, automation, and continuous monitoring that might not be feasible in-house.
What is the role of encryption in cloud security?
+Encryption is key to securing cloud data. It protects against unauthorized access by encrypting data at rest and in transit, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption keys.
How does cloud security differ from traditional IT security?
+Cloud security involves a shared responsibility model where both the cloud provider and the user manage different security aspects. It focuses on identity and access control, encryption, and security automation more than traditional IT security, which typically deals with on-premise infrastructure and perimeter security.
Related Terms:
- Cloud security best practices checklist
- Best practices security infrastructure
- Securing the cloud
- Cloud cybersecurity
- what are cloud security types
- why we need cloud security