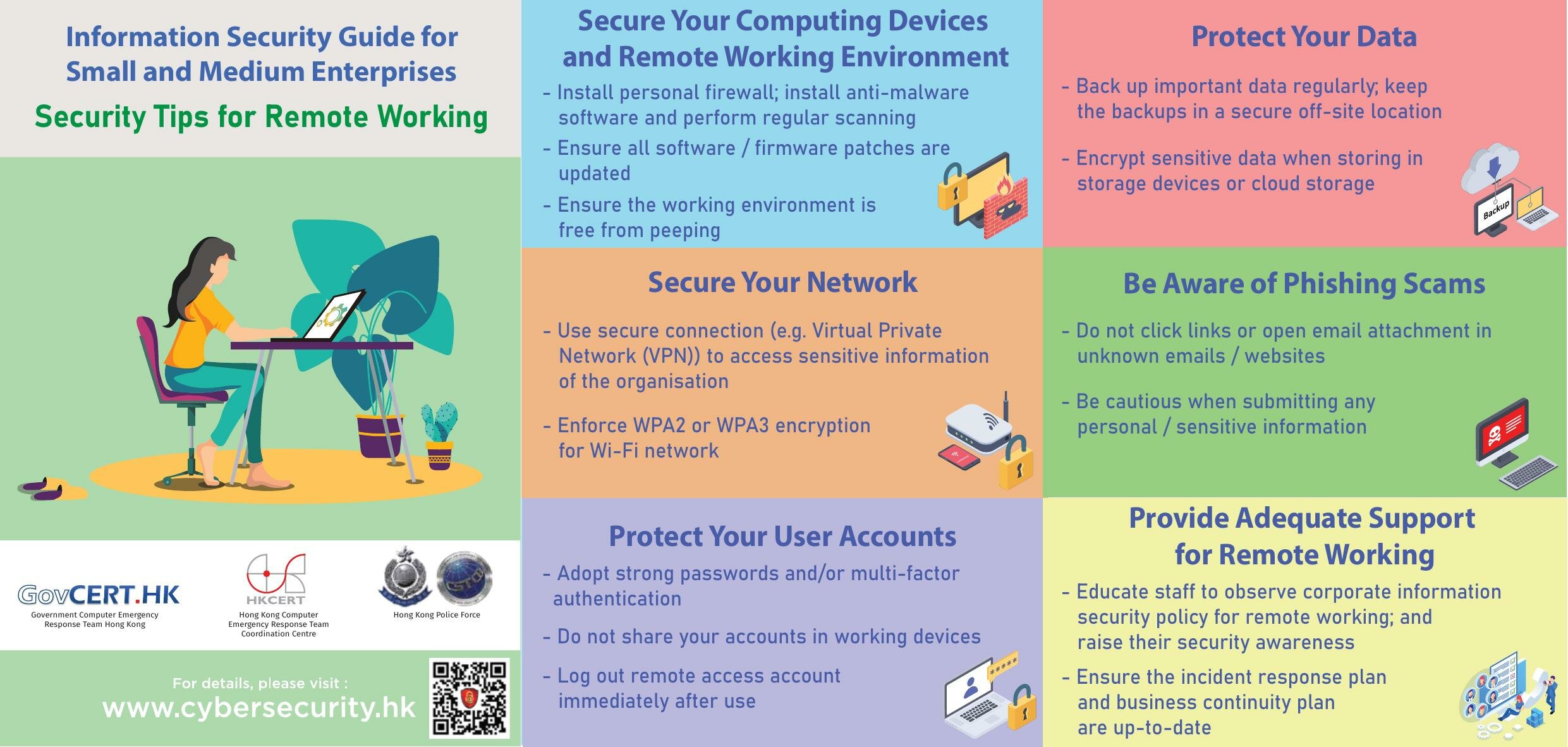
Cloud Computing Network Security Essentials

Securing your cloud environment is more critical than ever, as businesses across the globe rapidly adopt cloud computing technologies to enhance efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. With the migration of sensitive data and operations to the cloud, network security becomes a pivotal concern. Understanding the basics of cloud computing network security is essential for organizations looking to protect their assets from the myriad of cyber threats in this digital age.
What is Cloud Computing Network Security?
Cloud computing network security involves protecting the cloud infrastructure from unauthorized access, data breaches, service disruptions, and other threats. It encompasses the security policies, controls, and technologies that work together to safeguard data, applications, and infrastructure within the cloud environment.
Here are the key components of cloud computing network security:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): This ensures that the right individuals have the appropriate access to resources.
- Encryption: Encrypts data at rest and in transit to protect it from being compromised if intercepted.
- Network Security: Includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation to control traffic and secure network boundaries.
- Data Security: Focuses on protecting the integrity and confidentiality of data through backups, data loss prevention (DLP) tools, and data encryption.
- Security Management: Involves ongoing monitoring, incident response planning, and policy enforcement to maintain security posture.

Core Elements of Cloud Security
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM in cloud computing is crucial for controlling access to resources. It involves:
- User Authentication: Verifying user identity.
- Authorization: Determining what resources users can access.
- Identity Federation: Enabling secure sharing of identities with external systems.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding additional security layers to user authentication.
Encryption
Encryption is vital for securing data:
- At Rest: Data stored in cloud databases or storage systems is encrypted.
- In Transit: Data moving between endpoints is secured using protocols like TLS/SSL.
🔒 Note: While encryption provides strong security, it’s crucial to manage encryption keys securely to prevent unauthorized access.
Network Security Controls
These controls are designed to protect the network itself:
- Firewalls: Block or allow traffic based on defined rules.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): Monitor and respond to malicious activity or policy violations.
- Network Segmentation: Segments the network to isolate parts of the cloud environment from each other.
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPC): Logical constructs to create a private, isolated section of the cloud.
Best Practices for Securing Cloud Networks
Here are some best practices to enhance your cloud network security:
- Implement the Principle of Least Privilege: Users should only have access to what they need to perform their job functions.
- Use Security Groups and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): To fine-tune access to cloud resources.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Ensure all systems are up-to-date to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
- Deploy Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): For real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications.
- Continuously Monitor: Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to ensure compliance and security standards are met.
- Educate Your Team: Training is key; keep staff informed about security best practices.

Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider
The choice of cloud service provider (CSP) can significantly impact your security posture:
- Compliance and Certifications: Check for certifications like ISO 27001, SOC, or HIPAA compliance.
- Security Offerings: Evaluate what native security tools and features are provided by the CSP.
- Data Centers: Understand where data centers are located and their physical security measures.
- Incident Response: Assess how the CSP handles security incidents.
The landscape of cloud computing is ever-evolving, and as such, so too must your network security strategies. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes the elements discussed here, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to threats. Remember, security in the cloud is not just a technical challenge but also a governance and compliance issue. Regular assessments, training, and vigilant monitoring are crucial to ensuring that your cloud environment remains secure against evolving cyber threats.
Why is encryption important in cloud computing?
+Encryption safeguards data from unauthorized access by ensuring that even if data is intercepted or accessed, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys. It’s essential for maintaining data privacy and integrity in transit and at rest within cloud environments.
How does IAM contribute to cloud security?
+Identity and Access Management (IAM) ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources within the cloud. It controls who can log in, what they can do, and helps in maintaining a strong security posture by preventing unauthorized access or accidental data exposure.
What are some common security threats in cloud environments?
+Some common threats include data breaches, account hijacking, insecure APIs, misconfiguration, insider threats, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Each poses unique challenges to cloud security and requires specific countermeasures.
Related Terms:
- cloud basics for beginners
- cloud computing essential characteristics
- cloud computing essentials unlock benefits
- beginners guide to cloud computing
- cloud computing for beginners
- cloud computing essentials lumolog