5 Essential Network Security Tips for Cloud Computing
Understanding the Importance of Network Security in Cloud Computing
As organizations increasingly move their infrastructure to the cloud, the need for robust network security becomes even more critical. Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost savings, but it also introduces new security challenges. This blog post will dive into five essential network security tips to ensure that your cloud environment remains secure against threats.
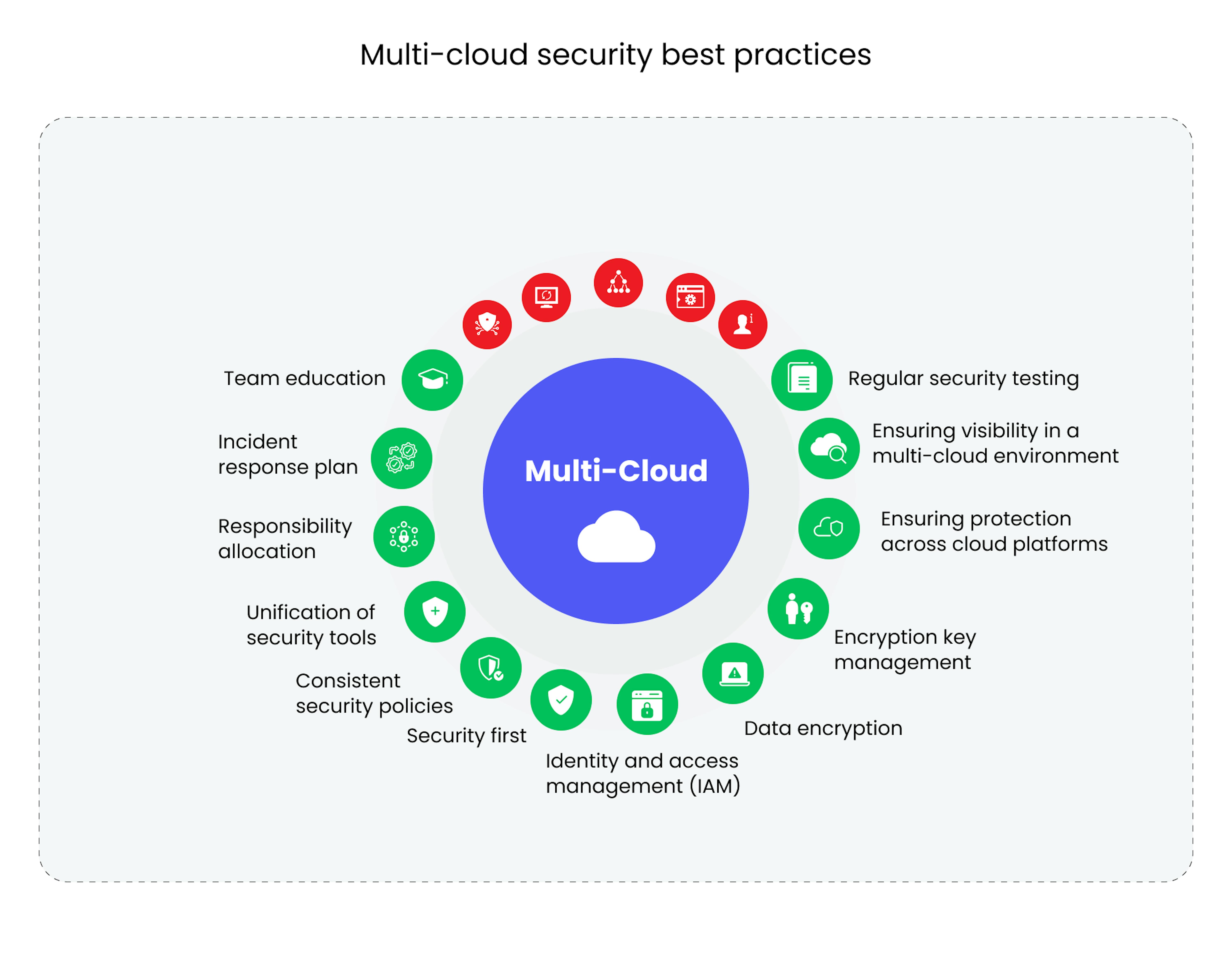
1. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
The first line of defense in cloud security is managing who can access your resources. Here are some practices:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to prove their identity in two or more ways. This could be something they know (like a password), something they have (like a mobile device), or something they are (biometrics).
- Least Privilege Access: Grant users the minimum levels of access—or permissions—they need to perform their jobs. This minimizes the potential damage if an account is compromised.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on the roles within your organization. Roles help in defining what each employee can do and what resources they can access.
2. Secure Data in Transit and at Rest
Securing data is paramount in cloud environments:
- Encryption: Use encryption for data both when it's being transmitted (in transit) and when stored (at rest). Technologies like SSL/TLS for transport and AES for storage encryption are standard.
- Key Management: Manage your encryption keys wisely. Consider using cloud provider's key management services or integrating third-party solutions that comply with standards like FIPS 140-2.
- Data Isolation: Isolate sensitive data to specific zones or regions, reducing the exposure if one part of the network gets breached.
⚠️ Note: Ensure that your encryption keys are stored securely and not accessible to unauthorized users or systems.
3. Regular Security Monitoring and Logging
Continuous monitoring and logging are vital for early threat detection:
- Implement SIEM: Security Information and Event Management systems help in real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications.
- Log Everything: Ensure all network activities are logged, from login attempts to file changes. This provides an audit trail for forensic analysis if a security breach occurs.
- Anomaly Detection: Use machine learning or artificial intelligence for anomaly detection, which can spot unusual activities that might signify a breach.
4. Maintain Software and Security Patches
Software vulnerabilities are a common entry point for attackers:
- Automate Updates: Automate the patch management process to ensure that all systems are up to date with the latest security patches.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly scan for vulnerabilities and prioritize patching based on the severity of the vulnerabilities found.
- Third-party Tools: Use third-party vulnerability assessment tools to gain insights into potential weaknesses in your cloud applications or infrastructure.
5. Educate and Train Your Workforce
Human error remains a significant risk factor:
- Security Awareness Training: Regularly train employees on security best practices, like identifying phishing attempts or the importance of strong passwords.
- Simulated Attacks: Conduct phishing simulation exercises to keep security at the forefront of your team's mind.
- Cloud Security Guidelines: Provide clear guidelines on how to handle data and resources in a cloud environment, including what to do in case of a suspected breach.
By weaving these five security tips into your cloud computing strategy, you are laying the groundwork for a robust defense against cyber threats. Each practice complements the others, creating a layered security approach that can adapt to evolving threats. Always remember that security is not a one-time setup but a continuous process of monitoring, updating, and educating.
Why is cloud computing less secure than on-premises infrastructure?
+Cloud computing isn’t inherently less secure than on-premises infrastructure. Security concerns stem from how organizations manage and configure their cloud environments. Proper implementation of security practices can make cloud environments just as secure, if not more so, due to the expertise of cloud service providers.
How often should we update our cloud security measures?
+Security measures should be reviewed and updated at least quarterly. However, with the rapid pace of cloud changes and threat evolution, having continuous monitoring and being prepared to make updates more frequently is advisable.
Can we outsource cloud security entirely?
+While cloud service providers offer robust security features, organizations are still responsible for their data and applications within the cloud. Security should be a shared responsibility model where the CSP handles the infrastructure, and you manage your application’s security.
Related Terms:
- how to improve network security